What are e-Payments?
By: Abinaya in Java Tutorials on 2007-09-14
e-Payments are secure real time payments that
transfer funds (via the Internet) between a consumer and the merchant's financial institutions.
e-Payments require secure communication between all components of the e-Payment process.
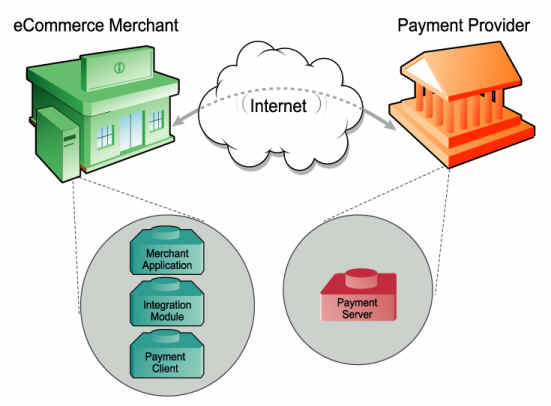
The Components of an e-Payment
Solution
An end-to-end e-Payment solution is made up
of the following components:
? The
Merchant application is a business
application/website on the merchant's system that uses Payment Client to process payments.
? The
Integration module is a communication bridge
between the merchant application and Payment Client.
? Payment
Client provides secure communication between the
merchant application and the Payment Server. Payment Client can be
integrated with a number of systems including merchant applications, Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
systems, and integrated ERPs
? Payment
Server processes merchant Digital Orders.
? The
Payment Provider enables the merchant to accept
payments online.
In their most simple form, e-Payments are represented in the following diagram:
How e-Payments Transfer Funds
e-Payments transfer funds via the following
steps:
1 The
cardholder purchases goods/services from the merchant (for example, in person,
via the
Internet, over the phone).
2 The merchant
application sends a Payment Client Digital Order (via the Payment Server) to the
merchant's Payment Provider.
3 The
merchant's Payment Provider directs the request to the cardholder's bank.
4 The
cardholder's bank debits the cardholder's account and transfers the funds to the
merchant's
account at the merchant's Payment Provider.
About e-Payment Information Flows
This section describes how information is
transferred between the merchant application and the
Payment Server.
The Merchant Application
To process a payment, the merchant
application must send the required information to the Payment
Server. The merchant application uses the
Payment Client to send this information to the Payment
Server using two messages:
? Digital
Order is sent by the Payment Client to the Payment
Server to provide transaction
information.
Digital Receipt is
sent from the Payment Server to the Payment Client to indicate the outcome of
the transaction (that is, successful or
otherwise).
? A Transaction
is the combination of a Digital Order and a
Digital Receipt. For each customer
purchase or order, merchants may issue
several transactions.
Payment Client
To securely communicate transaction
information between the merchant application and the Payment Server, the Payment Client:
? Formats,
encrypts and digitally signs a Digital Order from the merchant application; and
? Sends the
Digital Order to the Payment Server
? Receives the
Digital Receipt, decrypts it and processes the results.
The Payment Server
To complete the transaction the Payment
Server:
? Processes the
Digital Order
? Transfers
funds from the cardholder's account to the merchant's Payment Provider account
and
? Returns a
signed and encrypted Digital Receipt to Payment Client.
Add Comment
This policy contains information about your privacy. By posting, you are declaring that you understand this policy:
- Your name, rating, website address, town, country, state and comment will be publicly displayed if entered.
- Aside from the data entered into these form fields, other stored data about your comment will include:
- Your IP address (not displayed)
- The time/date of your submission (displayed)
- Your email address will not be shared. It is collected for only two reasons:
- Administrative purposes, should a need to contact you arise.
- To inform you of new comments, should you subscribe to receive notifications.
- A cookie may be set on your computer. This is used to remember your inputs. It will expire by itself.
This policy is subject to change at any time and without notice.
These terms and conditions contain rules about posting comments. By submitting a comment, you are declaring that you agree with these rules:
- Although the administrator will attempt to moderate comments, it is impossible for every comment to have been moderated at any given time.
- You acknowledge that all comments express the views and opinions of the original author and not those of the administrator.
- You agree not to post any material which is knowingly false, obscene, hateful, threatening, harassing or invasive of a person's privacy.
- The administrator has the right to edit, move or remove any comment for any reason and without notice.
Failure to comply with these rules may result in being banned from submitting further comments.
These terms and conditions are subject to change at any time and without notice.
- Data Science
- Android
- React Native
- AJAX
- ASP.net
- C
- C++
- C#
- Cocoa
- Cloud Computing
- HTML5
- Java
- Javascript
- JSF
- JSP
- J2ME
- Java Beans
- EJB
- JDBC
- Linux
- Mac OS X
- iPhone
- MySQL
- Office 365
- Perl
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- VB.net
- Hibernate
- Struts
- SAP
- Trends
- Tech Reviews
- WebServices
- XML
- Certification
- Interview
categories
Related Tutorials
Read a file having a list of telnet commands and execute them one by one using Java
Open a .docx file and show content in a TextArea using Java
Step by Step guide to setup freetts for Java
Of Object, equals (), == and hashCode ()
Using the AWS SDK for Java in Eclipse
DateFormat sample program in Java
concurrent.Flow instead of Observable class in Java
Calculator application in Java
Sending Email from Java application (using gmail)
Comments