How to export from DataGridView to excel using VB.net
By: Issac in VB.net Tutorials on 2009-02-21
For exporting data from Datagridview to Excel, connect the database and load data from the database to Datagridview and then create a new excel file and write the data from Datagridview to Excel file.
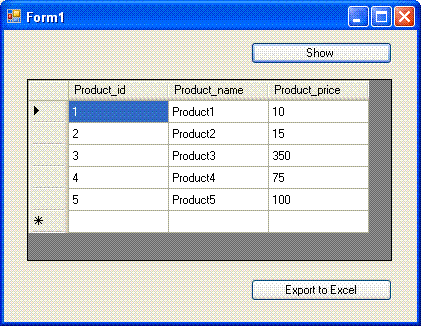
First step is to Load the Product table data to DataGridView, and create new Excel file and write the data from Datagridview to Excel file.
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
Imports Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles
Button1.Click
Dim cnn As SqlConnection
Dim connectionString As String
Dim sql As String
connectionString = "data source=servername;"
& _
"initial catalog=databasename;user
id=username;password=password;"
cnn = New
SqlConnection(connectionString)
cnn.Open()
sql = "SELECT * FROM
Product"
Dim dscmd As New SqlDataAdapter(sql,
cnn)
Dim ds As New DataSet
dscmd.Fill(ds)
DataGridView1.DataSource =
ds.Tables(0)
cnn.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
Dim xlApp As Excel.Application
Dim xlWorkBook As Excel.Workbook
Dim xlWorkSheet As Excel.Worksheet
Dim misValue As Object =
System.Reflection.Missing.Value
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
xlApp = New Excel.ApplicationClass
xlWorkBook =
xlApp.Workbooks.Add(misValue)
xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Sheets("sheet1")
For i = 0 To DataGridView1.RowCount -
2
For j = 0 To
DataGridView1.ColumnCount - 1
xlWorkSheet.Cells(i + 1, j + 1) = _
DataGridView1(j, i).Value.ToString()
Next
Next
xlWorkSheet.SaveAs("C:\vbexcel.xlsx")
xlWorkBook.Close()
xlApp.Quit()
releaseObject(xlApp)
releaseObject(xlWorkBook)
releaseObject(xlWorkSheet)
MsgBox("You can find the file
C:\vbexcel.xlsx")
End Sub
Private Sub releaseObject(ByVal obj As Object)
Try
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(obj)
obj = Nothing
Catch ex As Exception
obj = Nothing
Finally
GC.Collect()
End Try
End Sub
End Class
Add Comment
This policy contains information about your privacy. By posting, you are declaring that you understand this policy:
- Your name, rating, website address, town, country, state and comment will be publicly displayed if entered.
- Aside from the data entered into these form fields, other stored data about your comment will include:
- Your IP address (not displayed)
- The time/date of your submission (displayed)
- Your email address will not be shared. It is collected for only two reasons:
- Administrative purposes, should a need to contact you arise.
- To inform you of new comments, should you subscribe to receive notifications.
- A cookie may be set on your computer. This is used to remember your inputs. It will expire by itself.
This policy is subject to change at any time and without notice.
These terms and conditions contain rules about posting comments. By submitting a comment, you are declaring that you agree with these rules:
- Although the administrator will attempt to moderate comments, it is impossible for every comment to have been moderated at any given time.
- You acknowledge that all comments express the views and opinions of the original author and not those of the administrator.
- You agree not to post any material which is knowingly false, obscene, hateful, threatening, harassing or invasive of a person's privacy.
- The administrator has the right to edit, move or remove any comment for any reason and without notice.
Failure to comply with these rules may result in being banned from submitting further comments.
These terms and conditions are subject to change at any time and without notice.
- Data Science
- Android
- React Native
- AJAX
- ASP.net
- C
- C++
- C#
- Cocoa
- Cloud Computing
- HTML5
- Java
- Javascript
- JSF
- JSP
- J2ME
- Java Beans
- EJB
- JDBC
- Linux
- Mac OS X
- iPhone
- MySQL
- Office 365
- Perl
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- VB.net
- Hibernate
- Struts
- SAP
- Trends
- Tech Reviews
- WebServices
- XML
- Certification
- Interview
categories
Related Tutorials
Changes in Controls from VB6 to VB.net
Unstructured Exception Handling in VB.net
Structured Exception Handling in VB.net
Creating Sub Procedures in VB.net
Passing a Variable Number of Arguments to Procedures in VB.net
Specifying Optional Arguments with default values in Procedures in VB.net
Preserving a Variable's Values between Procedure Calls in VB.net
Throwing an Exception in VB.net
Comments