RMS Basics in J2ME
By: Daniel Malcolm in J2ME Tutorials on 2007-09-17
Each MIDP-compliant device maintains a dedicated area of device memory for persistent application data storage. MIDlet data stored here persists across multiple invocations of the applications that use it. Both the physical location and the size of the data store are device dependent.
The RMS API abstracts the device-dependent details of the storage area and access to those details, and it provides a uniform mechanism to create, destroy, and modify data. This ensures portability of MIDlets to different devices.
RMS Data Storage Model
The RMS supports the creation and management of multiple record stores, shown in Figure below. A record store is a database whose central abstraction is the record. Each record store consists of zero or more records. A record store name is case sensitive and can consist of a maximum of 32 Unicode characters. A record store is created by a MIDlet.
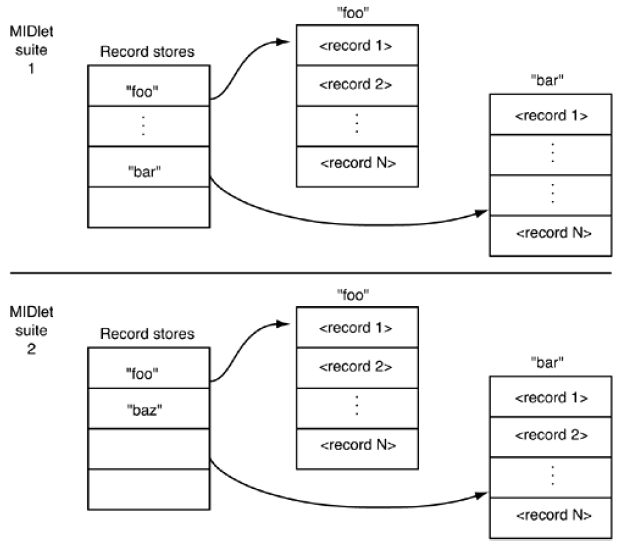
MIDlets within the same MIDlet suite can share one another's record stores. A MIDlet suite defines a name space for record stores; a record store must have a unique name within a MIDlet suite. The same name can be used in different MIDlet suites, however.
MIDlets can list the names of all the record stores available to them. They can also determine the amount of free space available for storing data. Incidentally, you should be aware that when all MIDlets in a MIDlet suite are removed from a device, the device AMS removes all record stores in the MIDlet suite namespace. All persistent data will be lost. For this reason, you should consider designing applications to include a warning or confirmation that requires users to acknowledge that they understand the potential loss of data when they remove applications. Applications might also include a mechanism to back up the records in a data store to another location. This might require server side support.
The RMS defines the following conceptual operations on an individual record store:
- Add a record.
- Delete a record.
- Change a record.
- Look up (retrieve) a record.
- Enumerate all records.
Records are uniquely identified by a record ID, which is the only primary key type supported. The type of all record ids is the Java built-in type int. The RMS has no support for features-such as tables, rows, columns, data types, and so forth-that are present in relational databases.
Records
A record is a byte array of type byte []. The RMS doesn't support the definition or formatting of fields within a record. Your application must define the data elements within a record and their format.
The reader of a record, therefore, must be aware of the format that was used to write the record. Because a record is simply a byte array, applications must convert data from arbitrary types to bytes when writing records, and they must convert from bytes to those types upon reading the data.
Here is a sample code that shows simple read and write of RMS in J2ME
import javax.microedition.midlet.*;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.*;
import javax.microedition.io.*;
import javax.microedition.rms.*;
public class ReadWriteRMS extends MIDlet{
private RecordStore rs = null;
static final String REC_STORE = "ReadWriteRMS";
public void startApp(){
openRecStore();
writeRecord("Core J2ME Technology");
writeRecord("J2ME Wireless Toolkit");
readRecords();
closeRecStore();
deleteRecStore();
}
public void pauseApp(){}
public void destroyApp(boolean unconditional){
notifyDestroyed();
}
public void openRecStore(){
try{
rs = RecordStore.openRecordStore(REC_STORE, true );
}catch (Exception e){}
}
public void closeRecStore(){
try{
rs.closeRecordStore();
}catch (Exception e){}
}
public void deleteRecStore(){
if (RecordStore.listRecordStores() != null){
try{
RecordStore.deleteRecordStore(REC_STORE);
}catch (Exception e){}
}
}
public void writeRecord(String str){
byte[] rec = str.getBytes();
try{
rs.addRecord(rec, 0, rec.length);
}catch (Exception e){}
}
public void readRecords(){
try{
byte[] recData = new byte[5];
int len;
for(int i = 1; i <= rs.getNumRecords(); i++){
if(rs.getRecordSize(i) > recData.length){
recData = new byte[rs.getRecordSize(i)];
}
len = rs.getRecord(i, recData, 0);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
System.out.println("Record " + i + " : " + new String(recData, 0, len));
System.out.println("------------------------------");
}
}catch (Exception e){}
}
} Add Comment
This policy contains information about your privacy. By posting, you are declaring that you understand this policy:
- Your name, rating, website address, town, country, state and comment will be publicly displayed if entered.
- Aside from the data entered into these form fields, other stored data about your comment will include:
- Your IP address (not displayed)
- The time/date of your submission (displayed)
- Your email address will not be shared. It is collected for only two reasons:
- Administrative purposes, should a need to contact you arise.
- To inform you of new comments, should you subscribe to receive notifications.
- A cookie may be set on your computer. This is used to remember your inputs. It will expire by itself.
This policy is subject to change at any time and without notice.
These terms and conditions contain rules about posting comments. By submitting a comment, you are declaring that you agree with these rules:
- Although the administrator will attempt to moderate comments, it is impossible for every comment to have been moderated at any given time.
- You acknowledge that all comments express the views and opinions of the original author and not those of the administrator.
- You agree not to post any material which is knowingly false, obscene, hateful, threatening, harassing or invasive of a person's privacy.
- The administrator has the right to edit, move or remove any comment for any reason and without notice.
Failure to comply with these rules may result in being banned from submitting further comments.
These terms and conditions are subject to change at any time and without notice.
- Data Science
- Android
- React Native
- AJAX
- ASP.net
- C
- C++
- C#
- Cocoa
- Cloud Computing
- HTML5
- Java
- Javascript
- JSF
- JSP
- J2ME
- Java Beans
- EJB
- JDBC
- Linux
- Mac OS X
- iPhone
- MySQL
- Office 365
- Perl
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- VB.net
- Hibernate
- Struts
- SAP
- Trends
- Tech Reviews
- WebServices
- XML
- Certification
- Interview
categories
Related Tutorials
GUI components and menu based J2ME Applications.
Code sample to Send SMS from a J2ME application.
Adding your own Application icon for your J2ME application (jar file)
Play a multimedia file in J2ME Program (Audio/Video) using MMAPI
Datagrams in J2ME (UDP Programming sample)
Client Server in J2ME (Socket Programming sample)
Using HttpConnection in J2ME (Retrieve web content from a website to a phone)
Using HTTP vs UDP vs Socket in J2ME
RMSCookieConnector - Using Cookies in J2ME
POST UTF-8 encoded data to the server in J2ME
Using alerts and tickers in J2ME
lists, forms, choices, gauges, text fields, text boxes in J2ME
Comments